🛠️ Root Cause Analysis (RCA): Techniques for Incident Managers
🔍 Introduction
When an incident disrupts IT operations, resolving it quickly is the priority. However, fixing the issue without understanding why it occurred can lead to recurring incidents. This is where Root Cause Analysis (RCA) comes in. RCA helps incident managers investigate the underlying cause of a problem rather than just addressing the symptoms.
In this blog, we will explore:
✅ What is Root Cause Analysis?
✅ Why is RCA important in incident management?
✅ Proven RCA techniques for effective troubleshooting
✅ Best practices for conducting RCA
📌 What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic process used to identify, analyze, and resolve the underlying cause of an incident. Instead of just fixing immediate symptoms, RCA ensures that long-term preventive actions are implemented.
🔥 Key Benefits of RCA in Incident Management
✅ Prevents recurring incidents by addressing the root cause
✅ Improves system reliability and operational efficiency
✅ Enhances team collaboration through structured problem-solving
✅ Reduces downtime and business impact

🔬 Proven RCA Techniques for Incident Managers
🛠 1. The 5 Whys Technique
A simple yet powerful RCA method where you ask “Why?” repeatedly until the root cause is identified.
🔹 Example:
📌 Incident: A website went down unexpectedly.
📌 Why #1? The server crashed.
📌 Why #2? CPU usage spiked to 100%.
📌 Why #3? A memory-intensive process consumed all resources.
📌 Why #4? A scheduled job ran without resource limitations.
📌 Why #5? No monitoring alerts were configured for resource consumption.
🎯 Root Cause: Lack of monitoring and resource allocation for scheduled jobs.
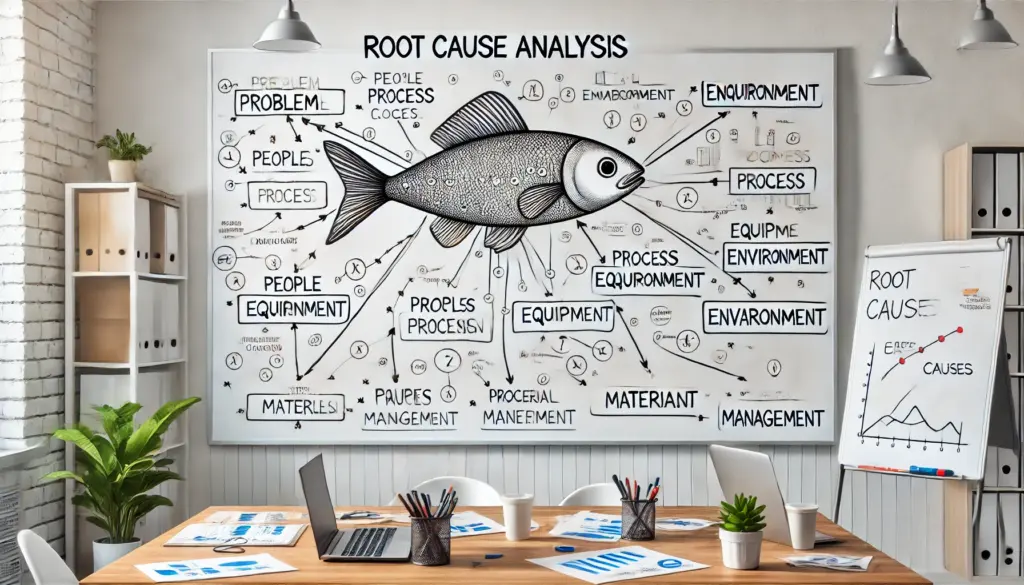
⚙️ 2. Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram)
A visual method to categorize potential root causes into key areas like People, Processes, Technology, and Environment.
💡 How to use it:
1️⃣ Define the problem (e.g., “System Slowness”).
2️⃣ Identify key factors (e.g., Network, Server, Application, Database).
3️⃣ Analyze sub-factors under each category to find contributing causes.
📊 3. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
A top-down approach to RCA where you start with the incident and break it down into possible causes.
💡 Example:
📌 Incident: Database outage
📌 Potential causes:
✔️ Hardware failure
✔️ Configuration issue
✔️ Network disconnection
✔️ Software bug
Each cause is further investigated until the root issue is identified.
🔄 4. Change Analysis
This method identifies recent changes in the system that might have triggered the incident.
💡 Steps:
✅ Identify all recent changes (e.g., software updates, configuration changes).
✅ Check for correlations between the change and the incident.
✅ Roll back or modify changes if needed.
📈 5. Pareto Analysis (80/20 Rule)
A statistical method to prioritize the most frequent issues affecting your system.
💡 Example:
If 80% of system crashes come from 20% of software bugs, focus on fixing those critical bugs first.
✅ Best Practices for Conducting RCA
🔹 Gather accurate incident data before starting RCA.
🔹 Collaborate with multiple teams (DevOps, IT Support, Security) for a holistic analysis.
🔹 Use monitoring tools like New Relic, Grafana, and ELK Stack for log analysis.
🔹 Document RCA findings to build a knowledge base for future reference.
🔹 Implement preventive actions to ensure the issue doesn’t occur again.
🚀 Conclusion
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a vital skill for Incident Managers, ensuring that incidents are not just resolved but prevented from happening again. By using structured RCA techniques like 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagrams, and Change Analysis, you can enhance your problem-solving capabilities and contribute to a more stable IT environment.
🚀Learn More:
Would you like to learn more about advanced RCA techniques or real-world RCA case studies? Drop your thoughts in the comments!




