An Introduction to Security Incident Management
🔍 Introduction
Security Incident Management: Cyber threats are increasing daily, and no organization is immune to security incidents. From data breaches to malware attacks, businesses must have a structured approach to detect, respond, and recover from security threats.
This is where Security Incident Management (SIM) comes into play. It ensures organizations can quickly identify, mitigate, and learn from security incidents to protect their systems and data.
📌 In this guide, you’ll learn:
✔️ What Security Incident Management is and why it’s essential
✔️ The security incident lifecycle and response steps
✔️ Best practices to improve security response and recovery
✔️ Tools and automation techniques to strengthen your security posture

🛡️ What is Security Incident Management?
Security Incident Management (SIM) is the structured process of detecting, responding to, and mitigating security threats and breaches in an IT environment.
🚀 Why is it important?
🔹 Helps prevent data breaches and cyberattacks
🔹 Minimizes downtime and business disruption
🔹 Ensures compliance with security regulations
🔹 Strengthens overall cybersecurity defenses
Security incidents can range from minor phishing attempts to major ransomware attacks affecting an entire organization. The key is to detect and respond quickly before damage spreads.
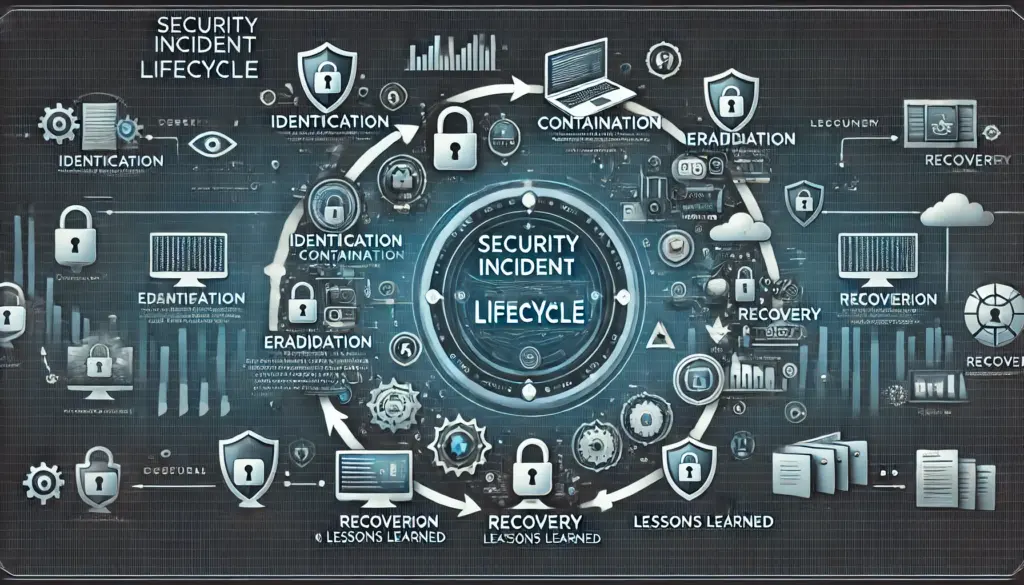
🔥 The Security Incident Lifecycle
A structured incident response plan follows a lifecycle approach to managing security threats effectively.
📍 1. Identification & Detection
🔍 Recognizing potential security threats using monitoring tools.
✔️ Real-time alerts from SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tools
✔️ Analyzing unusual user activity, login attempts, and system behavior
✔️ Incident reports from employees or external threat intelligence
Example: If an employee receives a phishing email, the security team must identify the risk before it leads to unauthorized access.
🛑 2. Containment & Mitigation
Once a security incident is detected, the next step is damage control.
✔️ Isolate affected systems to prevent the spread of malware
✔️ Block compromised user accounts to limit unauthorized access
✔️ Disable network access if required to contain the breach
📌 Example: If a DDoS attack is flooding the network, redirect traffic through Cloudflare or AWS Shield to prevent downtime.

🔍 3. Investigation & Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
After containment, security analysts must determine the cause and scope of the attack.
✔️ Analyze security logs to trace the attack path
✔️ Check for unauthorized access, file modifications, or malware installations
✔️ Use forensic tools to assess data exfiltration or compromise
📌 Example: If a data breach occurs, security teams should investigate which systems were accessed and what data was compromised.
🔄 4. Eradication & Recovery
Once the root cause is identified, take steps to fully remove the threat and restore affected systems.
✔️ Patch vulnerabilities in applications and servers
✔️ Restore from clean backups if data is compromised
✔️ Conduct system-wide security scans to ensure no traces remain
📌 Example: If an attacker exploited an unpatched software vulnerability, apply security updates immediately to prevent future breaches.
📑 5. Postmortem & Lessons Learned
After resolving the incident, the final step is learning from the event to improve future security.
✔️ Conduct a post-incident review with all stakeholders
✔️ Document key findings and improvements needed
✔️ Update security policies and training programs
📌 Pro Tip: Keep an incident knowledge base to track common security threats and response actions.
🔧 Best Practices for Security Incident Management
🛠️ 1. Use Advanced Monitoring & SIEM Tools
Having real-time visibility is crucial for early detection of threats.
🔹 SIEM Tools: Splunk, IBM QRadar, Microsoft Sentinel
🔹 Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR): CrowdStrike, SentinelOne, Sophos
🔹 Network Security Monitoring: Snort, Suricata, Zeek
📌 Pro Tip: Set up automated alerts for unusual login activity, privilege escalations, or network intrusions.
🔒 2. Implement Strong Access Controls
Access control is a fundamental defense against security breaches.
✔️ Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all critical systems
✔️ Follow the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) – grant only necessary access
✔️ Regularly review and update user permissions
📌 Example: If an employee leaves the company, immediately revoke access to prevent potential insider threats.
🚀 3. Automate Security Incident Response
Automation helps respond faster and reduces human errors.
✔️ Use Automated Threat Detection to identify risks in real time
✔️ Set up Auto-Containment Rules to block malicious IPs instantly
✔️ Deploy Self-Healing Systems to restore compromised files
📌 Example: AWS Lambda functions can automatically quarantine infected servers when a security threat is detected.
🔥 Building a Security-First Culture
Beyond tools and processes, a security-aware culture is essential to prevent incidents.
✔️ Conduct regular cybersecurity awareness training for employees
✔️ Perform simulated phishing attacks to test staff readiness
✔️ Encourage a “report-first” approach for suspicious activities
📌 Pro Tip: Create a Cybersecurity Playbook so employees know how to respond to different types of attacks.
🚀 Final Thoughts
Effective Security Incident Management is crucial for protecting organizations from cyber threats and ensuring business continuity.
💡 Key Takeaways:
✔️ Detect threats early with SIEM and EDR tools
✔️ Respond quickly with automated security workflows
✔️ Implement access control and strong authentication
✔️ Continuously improve security response plans
📢 Next Steps:
🔹 Conduct a cybersecurity drill to test your response plan.
🔹 Implement multi-layered security for enhanced protection.
🔹 Start using AI-powered threat detection for real-time alerts.
🚀Learn More:
💬 Have questions about security incident management? Drop them in the comments below!