Advanced Root Cause Analysis Techniques
🛠️ Introduction
In the fast-paced world of incident management, quickly identifying and resolving the root cause of an issue is critical to maintaining system reliability and minimizing downtime. Basic RCA techniques like the 5 Whys or Ishikawa diagrams work well for simple problems, but for complex, recurring, or high-impact incidents, you need more advanced RCA methodologies.
In this blog, we’ll explore advanced root cause analysis techniques used by top incident managers to diagnose and prevent major IT incidents.

🕵️ What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic process used to identify the primary reason an incident occurred, rather than just addressing its symptoms. The goal is to implement permanent fixes rather than temporary workarounds.
Benefits of RCA in Incident Management:
✅ Minimizes recurring incidents by addressing the underlying issue
✅ Reduces downtime by improving resolution efficiency
✅ Enhances system reliability and stability
✅ Improves communication between IT, DevOps, and business teams
🔍 Key Challenges in Root Cause Analysis
Even with well-defined RCA processes, IT teams face several challenges:
📌 Complex IT environments – Multiple interdependent services make issue tracking difficult
📌 Data overload – Large logs and monitoring data make it hard to pinpoint issues
📌 Lack of historical insights – Missing past RCA documentation can slow down investigations
📌 Hidden dependencies – Issues may arise from external APIs, cloud providers, or microservices
To overcome these challenges, advanced RCA techniques leverage data analytics, automation, and structured methodologies.

🚀 Advanced Root Cause Analysis Techniques
1️⃣ Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Best for: Identifying potential failures before they happen
How It Works:
FMEA is a proactive approach that helps identify and prioritize potential failure points in a system before they cause incidents.
🔹 Step 1: Identify components, processes, or systems prone to failure
🔹 Step 2: Determine the possible ways each component can fail
🔹 Step 3: Assess the severity (S), occurrence (O), and detection (D) of each failure
🔹 Step 4: Calculate the Risk Priority Number (RPN) = S × O × D
🔹 Step 5: Address the highest-risk areas first
✅ Example: A cloud service provider uses FMEA to evaluate database replication failure risks and implements redundancy measures before an issue occurs.
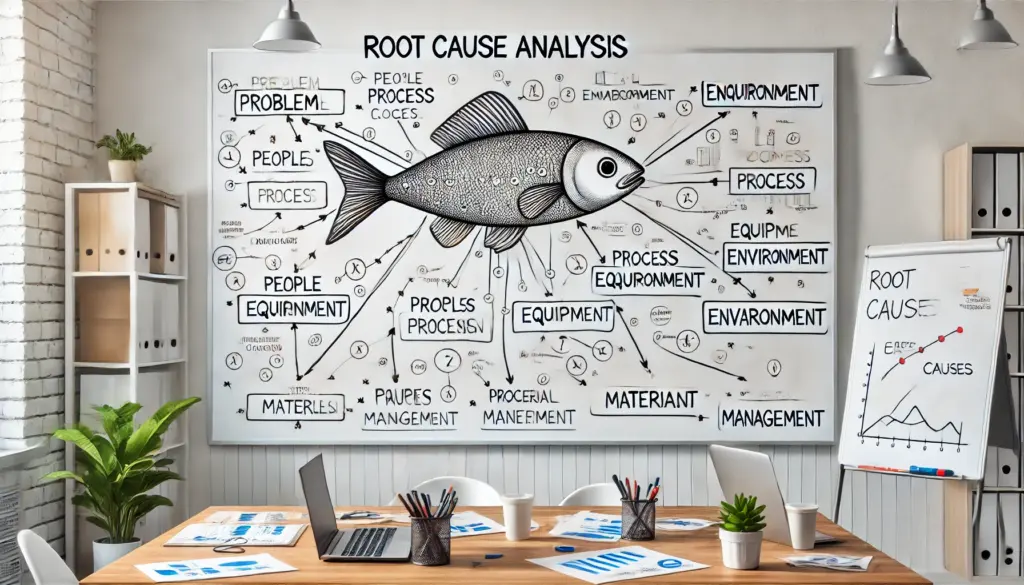
2️⃣ Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa) + AI-driven Insights
Best for: Categorizing possible causes of an incident efficiently
How It Works:
The Fishbone Diagram categorizes root causes into groups such as:
🔹 People – Human errors, lack of training
🔹 Process – Poor workflows, missing automation
🔹 Technology – Software bugs, server failures
🔹 External Factors – Vendor issues, cyberattacks
With AI-driven RCA tools like New Relic, Dynatrace, or Splunk, incident managers can automate data collection and anomaly detection, making Fishbone analysis faster and more precise.
✅ Example: AI-powered anomaly detection flags memory leaks in an application, reducing the time spent manually investigating logs.
3️⃣ Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
Best for: Analyzing critical system failures in a hierarchical structure
How It Works:
FTA is a top-down, logical approach that visualizes how different failures contribute to an incident. It starts with a main failure event and branches out into possible causes, forming a tree-like structure.
🔹 Step 1: Identify the primary failure event
🔹 Step 2: Break down all contributing failure modes
🔹 Step 3: Use logical operators (AND, OR, NOT) to analyze dependencies
🔹 Step 4: Identify and fix the most critical failure points
✅ Example: A financial application experiences delayed transactions. Using FTA, the incident team traces the issue to database query timeouts caused by an overloaded API gateway.
4️⃣ Timeline Analysis & Event Correlation
Best for: Investigating highly complex incidents spanning multiple services
How It Works:
By creating a detailed incident timeline, engineers can correlate events across different logs, monitoring tools, and system components.
🔹 Step 1: Collect logs, error reports, and monitoring data
🔹 Step 2: Align events chronologically to detect causal relationships
🔹 Step 3: Identify patterns or recurring failures
🔹 Step 4: Use event correlation tools like Splunk, Datadog, or Elastic Stack to automate analysis
✅ Example: A server crash at 3:45 AM correlates with a spike in CPU usage at 3:30 AM, which traces back to a scheduled backup job consuming excessive resources.
5️⃣ Machine Learning-Powered RCA (AIOps)
Best for: Automating RCA and predicting future failures
How It Works:
Machine Learning (ML) and AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations) use historical incident data, real-time logs, and monitoring metrics to automatically detect root causes and predict failures before they occur.
🔹 AI-driven log analysis – Detects patterns in logs to pinpoint failure causes
🔹 Predictive analytics – Identifies systems at risk of failure before an incident occurs
🔹 Automated anomaly detection – Flags unusual behavior across servers, databases, and microservices
✅ Example: An ML model detects that server failures increase 10x when memory usage exceeds 80%, leading engineers to proactively optimize memory allocation.
📝 Best Practices for Implementing Advanced RCA
🔹 Integrate monitoring tools like Grafana, New Relic, and Prometheus for real-time insights
🔹 Document every RCA process for continuous improvement
🔹 Conduct RCA training to build a culture of problem-solving
🔹 Automate incident correlation using AI-based tools
📝 FAQs on Advanced Root Cause Analysis Techniques
1️⃣ What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in incident management?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic approach used to identify the underlying cause of an incident rather than just addressing its symptoms. The goal is to implement permanent solutions that prevent future occurrences.
2️⃣ Why is RCA important in IT incident management?
RCA is crucial because it helps:
✅ Minimize recurring issues
✅ Reduce downtime and improve system stability
✅ Enhance troubleshooting efficiency
✅ Improve team collaboration and decision-making
3️⃣ What are the biggest challenges in conducting RCA?
Some key challenges include:
📌 Complex IT environments with multiple dependencies
📌 Large volumes of logs and monitoring data
📌 Lack of historical RCA documentation
📌 Hidden dependencies on external services
4️⃣ What are the most effective advanced RCA techniques?
Some of the best advanced RCA techniques include:
🔹 Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) – Identifying potential failures proactively
🔹 Fishbone Diagram + AI-driven insights – Categorizing root causes effectively
🔹 Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) – Visualizing dependencies and failure points
🔹 Timeline Analysis & Event Correlation – Tracking incidents across multiple systems
🔹 AIOps & Machine Learning-powered RCA – Automating root cause detection
5️⃣ How does Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) help in RCA?
FMEA helps teams identify and prioritize risks before failures happen. It evaluates:
✔️ Severity of failure
✔️ Occurrence probability
✔️ Detection difficulty
By calculating the Risk Priority Number (RPN), teams can address the most critical failure points first.
6️⃣ What is a Fishbone Diagram, and how does AI enhance it?
A Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa) categorizes root causes into groups such as People, Process, Technology, and External Factors.
✅ AI-powered tools like Splunk, New Relic, and Dynatrace automate log analysis and anomaly detection, making RCA more efficient.
7️⃣ How does Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) improve RCA?
FTA is a top-down approach that maps out how smaller failures contribute to a major incident. It helps teams visualize:
✔️ Failure dependencies using logical operators (AND, OR, NOT)
✔️ The most probable failure points in complex systems
8️⃣ What role does event correlation play in RCA?
Event correlation tools like Datadog, Elastic Stack, and Splunk help track incident timelines across multiple services.
🔍 Example: A database outage at 3:45 AM correlates with a CPU spike at 3:30 AM, indicating a resource exhaustion issue.
9️⃣ What is AIOps, and how does it improve RCA?
AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations) uses Machine Learning to:
✔️ Detect anomalies in real-time
✔️ Analyze logs automatically
✔️ Predict future failures
By leveraging AIOps, teams reduce the time spent manually analyzing logs.
🔟 What are the best tools for conducting RCA in IT incident management?
Some of the top tools include:
🛠️ Monitoring & Logging: Grafana, New Relic, Prometheus
🛠️ Incident Analysis: Splunk, Datadog, Elastic Stack
🛠️ Event Correlation: Moogsoft, BigPanda, Dynatrace
🛠️ AIOps & RCA Automation: LogicMonitor, ScienceLogic
11️⃣ How can teams implement an effective RCA process?
To implement a strong RCA process:
🔹 Standardize RCA documentation for knowledge sharing
🔹 Integrate AI-driven monitoring and log analysis tools
🔹 Conduct regular RCA training for incident response teams
🔹 Use automated event correlation to detect patterns faster
12️⃣ How often should RCA be performed?
RCA should be conducted after every major incident or recurring issues that impact system performance. Proactive RCA (using FMEA) can be done regularly to prevent failures before they occur.
13️⃣ How does RCA differ from incident resolution?
📌 Incident resolution focuses on quickly fixing an issue to restore service.
📌 RCA investigates why the incident occurred to prevent it from happening again.
14️⃣ Can RCA be fully automated?
While some RCA tasks can be automated using AI, log analysis, and event correlation tools, human expertise is still required to interpret findings, validate root causes, and implement corrective actions.
📌 Conclusion
Advanced Root Cause Analysis Techniques allow incident managers to move beyond basic troubleshooting and implement proactive, data-driven problem-solving strategies.
✅ Key Takeaways:
✔️ Use FMEA to predict failures before they occur
✔️ Leverage AI-powered Fishbone Diagrams for fast categorization
✔️ Implement Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) for structured problem-solving
✔️ Utilize event correlation tools for multi-service incident tracking
✔️ Adopt AIOps & ML-driven RCA for automated root cause detection
By mastering these advanced RCA techniques, IT teams can significantly reduce incident resolution time and enhance overall system resilience. 🚀
📚 Learn More:
💬 What RCA technique has worked best for you? Let’s discuss in the comments!