Incident Management Career Roadmap: Your Path to Success in IT Operations
Introduction to Incident Management
Definition and Importance of Incident Management
Incident Management is a critical aspect of IT operations that ensures systems are restored quickly following any disruption, minimizing business impact. This career path offers professionals the opportunity to specialize in managing incidents, improving system reliability, and enhancing organizational resilience.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
- Incident Analysts: Investigate, document, and resolve incidents.
- Incident Managers: Oversee incident management processes and ensure timely resolution.
- Senior Incident Managers: Lead and strategize incident management efforts at a high level.
Incident Management Lifecycle Overview
Incident Management follows a structured lifecycle:
- Detection: Identifying the incident.
- Response: Initial actions to mitigate the impact.
- Resolution: Restoring services and preventing recurrence.
- Recovery: Returning to normal operations.
- Post-Incident Review: Evaluating the effectiveness and lessons learned.
1. Basic Level (Foundational Skills)
To start your career in Incident Management, you’ll need to develop foundational knowledge and skills in IT operations.
Understanding ITIL Framework
The ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) framework is key to Incident Management. It covers core principles like Incident, Problem, and Change Management. Gaining a basic understanding of ITIL will help you navigate incidents efficiently.
Basic Technical Skills
- Networking Fundamentals: Learn about networks, protocols, and troubleshooting.
- System Basics: Familiarize yourself with operating systems such as Windows and Linux.
- Basic Scripting: Develop simple scripts (Bash or PowerShell) to automate tasks.
Incident Detection and Reporting
Tools like Freshdesk and ServiceNow are vital in detecting, reporting, and tracking incidents. Familiarity with these tools is essential at the basic level.
Soft Skills
Effective communication, teamwork, and problem-solving skills are essential for collaborating with teams and resolving incidents quickly.

2. Intermediate Level (Developing Proficiency)
At this stage, you’ll be refining your skills and developing expertise in more advanced tools and strategies.
Incident Triage and Prioritization
Analyzing the severity and impact of an incident is crucial. You’ll need to understand how to triage incidents effectively and prioritize based on business needs.
Advanced Monitoring Tools
- New Relic, Grafana, Nagios, ELK Stack: These tools help monitor systems in real-time and alert you about issues. Mastering them will allow you to quickly identify incidents.
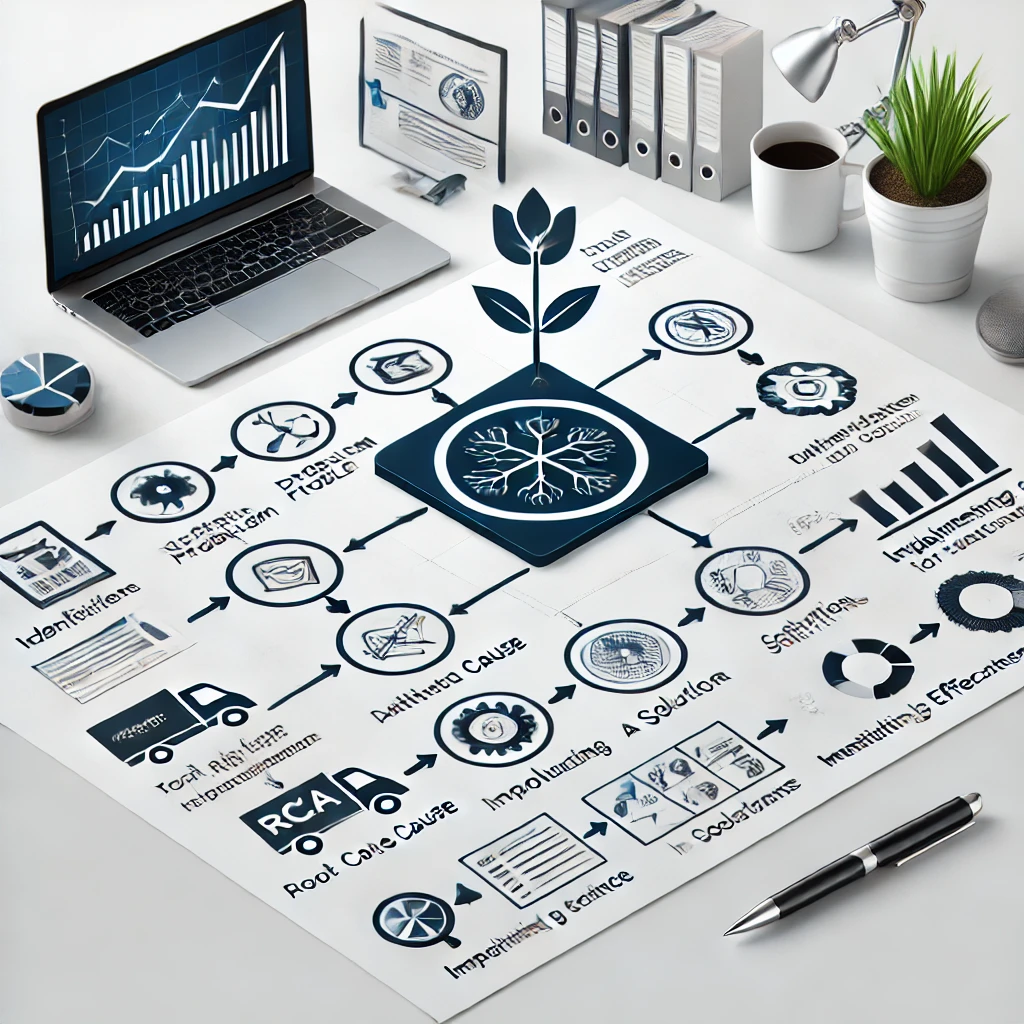
Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Learning to perform a Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is key to identifying the cause of recurring incidents and preventing future disruptions.
Automation Basics
- Introduction to Jenkins for CI/CD automation.
- Basic automation scripting to streamline incident management.
Collaboration with Cross-functional Teams
Effective incident management requires collaboration with developers, system admins, and business teams. Learn how to work with different teams to solve complex problems.

3. Advanced Level (Expertise Building)
At this level, you’ll develop deep expertise in incident response, security, and advanced tools.
Incident Response and Recovery
Create incident response playbooks, plan for disaster recovery, and execute recovery processes to restore service as quickly as possible.
Security Incident Management
Gain proficiency in security tools (SIEM, security protocols) and learn how to handle security incidents that could impact your organization.
Performance Optimization
Learn about system tuning, application performance management, and how to identify and resolve performance bottlenecks.
Advanced Automation
- Implement CI/CD pipelines to automate incident management processes.
- Understand Infrastructure as Code (IaC) concepts to enhance scalability and reduce human error.
Metrics and Reporting
Track SLAs (Service Level Agreements), SLOs (Service Level Objectives), and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) to measure incident management performance and improvement.

4. Expert Level (Leadership and Strategy)
At the expert level, you’ll move beyond technical expertise and lead incident management strategy within your organization.
Incident Management Strategy
Design and optimize incident management processes to enhance overall system reliability. This includes creating frameworks for efficient incident resolution and continuous improvement.
Crisis Management
Learn how to handle high-severity incidents and crisis communications to ensure that all stakeholders are informed and services are restored quickly.
Leadership Skills
- Lead and mentor incident management teams.
- Develop strategic planning skills to align incident management with business goals.
Business Continuity Planning
Ensure resilience in your organization by preparing for disasters and ensuring that critical operations continue without disruption.
Certifications
- ITIL Expert
- Certified Incident Handler (CIH)
- PMP (Project Management Professional) for leadership roles.
5. Continuous Learning and Growth
Incident Management professionals must stay updated with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices.
- Attend workshops and webinars on incident management and IT operations.
- Engage with industry communities and forums for networking and knowledge exchange.
- Stay updated on emerging technologies like Cloud Computing, DevOps, and AI-based automation.
6. Certifications Roadmap
- ITIL Foundation (Basic Level): Learn the fundamentals of Incident Management.
- CompTIA Security+ (Intermediate): Strengthen your knowledge in security concepts.
- Certified Incident Handler (Advanced): Specialize in handling complex incidents.
- ITIL Expert, PMP (Expert Level): Achieve leadership roles and strategic management.
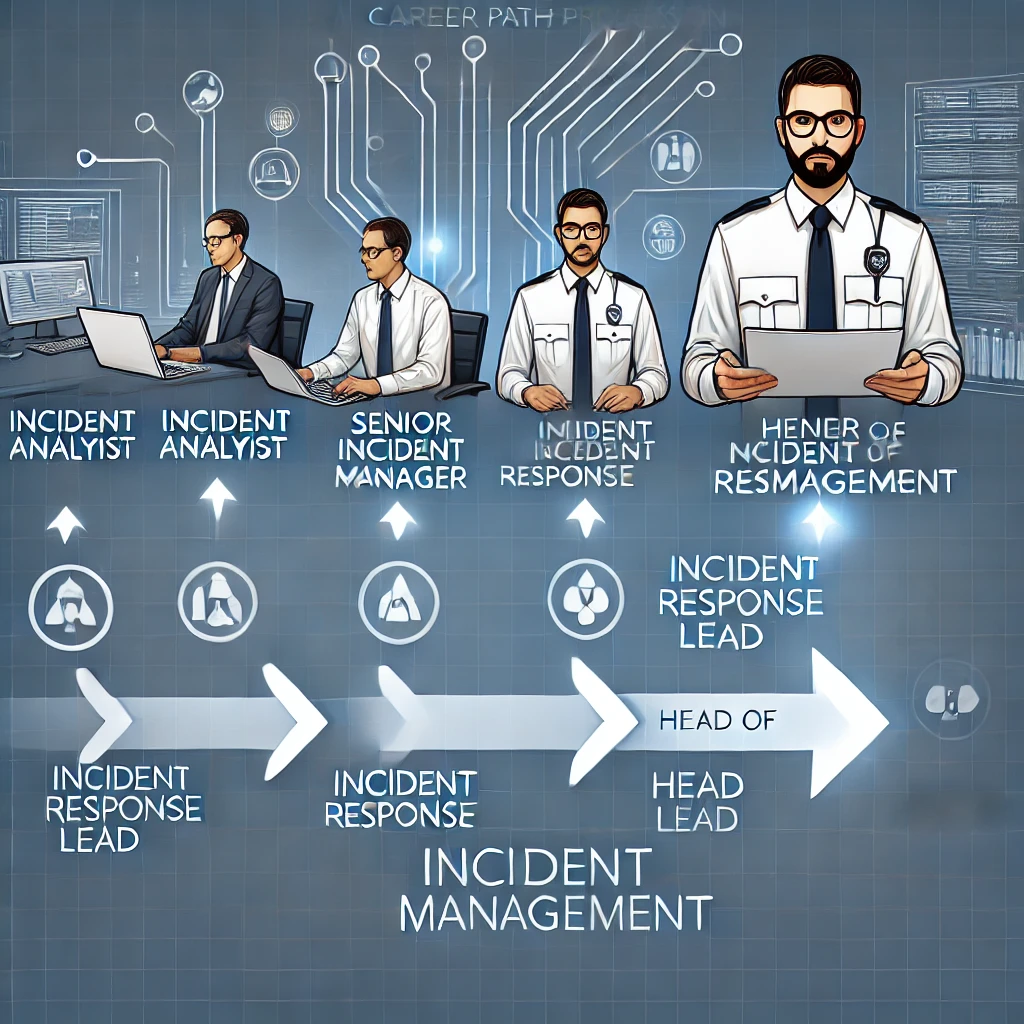
7. Career Path Progression
As you progress in your career, you’ll move from hands-on technical roles to leadership and strategy-focused positions.
- Incident Analyst → Incident Manager → Senior Incident Manager → Incident Response Lead → Head of Incident Management
Conclusion
Incident Management is a rewarding career path that offers opportunities for growth in both technical and leadership roles. By following this roadmap, you can gain the necessary skills, certifications, and experience to excel in the field. Continuous learning and professional development will ensure that you stay ahead in the fast-paced world of IT incident management.
Ready to start your Incident Management career? Follow the roadmap, gain the essential skills, and watch your career soar to new heights!




